- Services
- Rise In Creatinine
- Leakage Of Protein In Urine ( Nephrotic/Nephritic Syndrome)
- Blood In Urine
- Rapidly Progressive Renal Failure
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) & Its Related Kidney Complications
- Diabetes & It's Related Kidney Complications
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Chronic Kidney Injury & Its Complications
- Kidney Dialysis Therapy (Hemodialysis And Peritoneal Dialysis)
- Glomerulonephritis
- Kidney Stone & It’s Medical Management
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Prostate Related Problems
- Kidney Transplant & It’s Complications
- Interventional Nephrology - Renal Biopsy - Dialysis Catheter (Temporary & Tunnelled Catheters)
- Critical Care Nephrology (ICU Related Kidney Disorders)
- Fluids & Electrolyte Disorders
- Acid Base Disorder
- Onconephrology (Cancer Related Kidney Disorders)
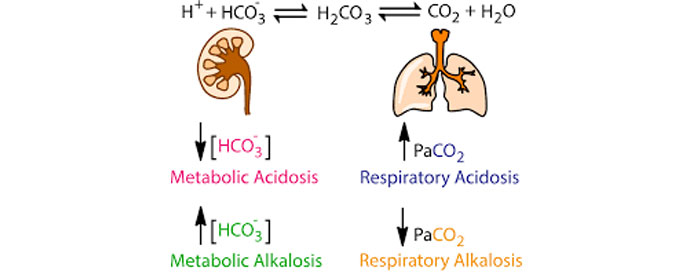
Acid Base Disorder
Ah, the delicate dance of acids and bases in the body! Let's waltz into the world of acid-base disorders.
Normal Acid-Base Balance
Our body works hard to maintain a slightly alkaline pH, hovering around 7.4. This balance is crucial for enzyme function, cellular processes, and overall physiological stability.
Acid-Base Disorders
1. Respiratory Acidosis- Cause: Inadequate removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) by the lungs, leading to increased levels of carbonic acid in the blood.
- Symptoms: Respiratory distress, confusion, and, in severe cases, respiratory failure.
- Causes: Lung diseases (COPD, pneumonia), airway obstruction, drug overdose.
- Cause: Excessive removal of CO2 by the lungs, leading to decreased carbonic acid levels.
- Symptoms: Hyperventilation, dizziness, and tingling in extremities.
- Causes: Anxiety, fever, hyperventilation, early stages of high-altitude exposure.
- Cause: Increased production of acids or inadequate removal of acids by the kidneys, leading to decreased bicarbonate levels.
- Symptoms: Deep, rapid breathing (Kussmaul breathing), confusion, and, in severe cases, shock.
- Causes: Diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, severe diarrhea, kidney disease.
- Cause: Loss of acids or excessive intake of alkaline substances, leading to increased bicarbonate levels.
- Symptoms: Muscle twitching, hand tremors, and, in severe cases, seizures.
- Causes: Vomiting, excessive use of diuretics, prolonged use of antacids.
Diagnostic Tools
1. Blood Gas Analysis- Measures pH, partial pressure of oxygen (PO2), partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2), and bicarbonate levels.
- Assesses serum electrolytes, including bicarbonate, sodium, and potassium.
- Consideration of symptoms, medical history, and potential causes.
Management
1. Treat Underlying Cause- Identifying and addressing the root cause is crucial for resolving acid-base disorders.
- Balancing electrolytes through intravenous fluids.
- In cases of respiratory acidosis or alkalosis, respiratory support may be necessary.
- Managing medications that may contribute to acid-base imbalances.
Understanding acid-base disorders is like reading the body's pH diary. It helps healthcare professionals pinpoint issues and choreograph interventions to bring the dance back into harmony.